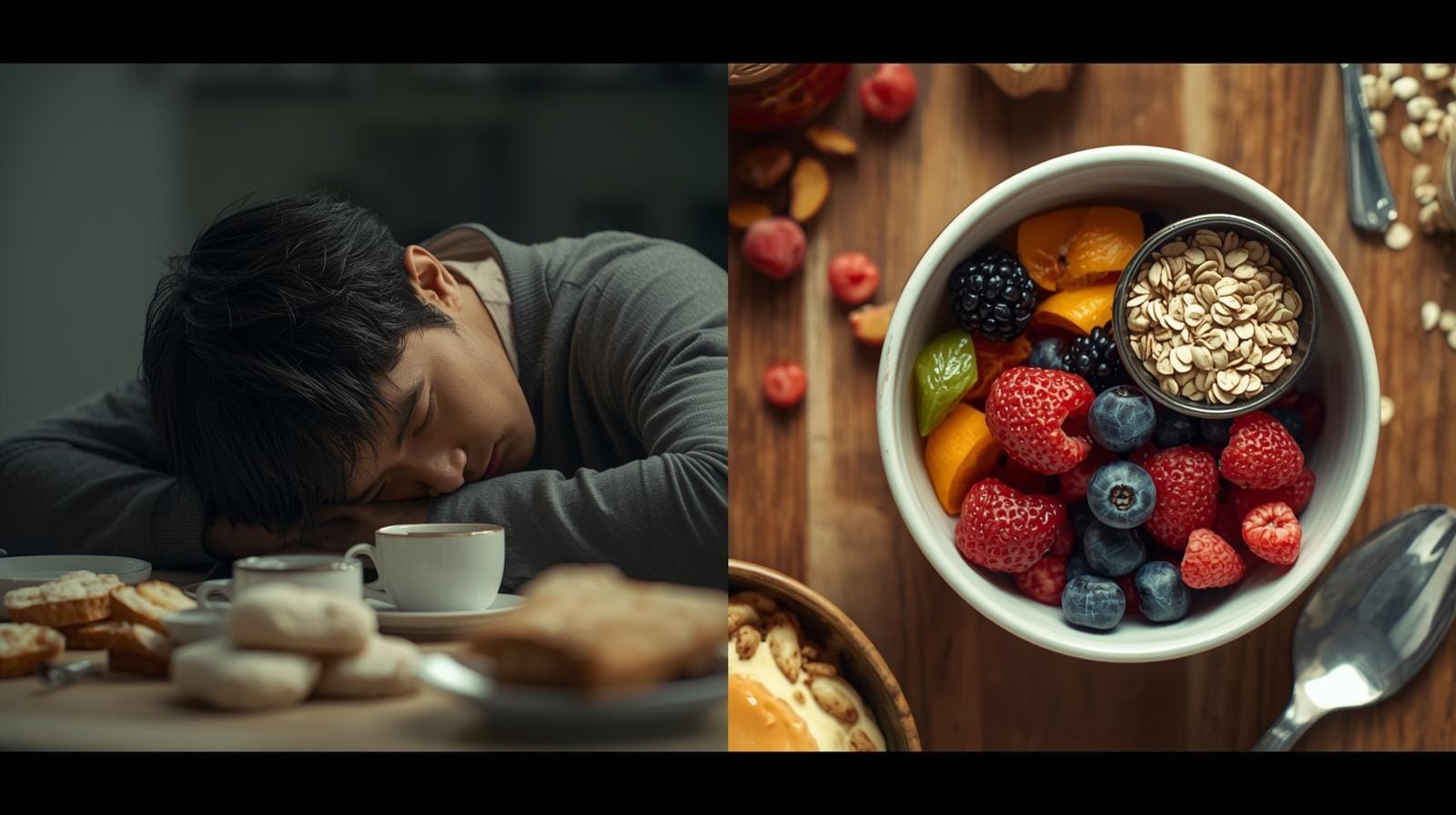
Energy crashes are something almost everyone deals with. You feel fine one moment, then suddenly you’re tired, foggy, hungry, or dragging through the rest of the day. It’s easy to blame sleep or stress, but many crashes come from one simple cause: not enough fiber.
Fiber affects digestion, blood sugar, hormones, and even the bacteria in your gut. When your fiber intake is too low, your energy levels become unstable throughout the day.
Understanding how fiber supports steady energy can help you build meals that keep you full, focused, and energized without relying on caffeine or sugar.
How Fiber Supports Steady Energy
Fiber helps keep your energy stable by slowing down how you digest and absorb food. When you eat foods with fiber, everything moves through your system at a more controlled pace, which keeps your energy steady.
Slows Digestion for Longer-Lasting Fuel
Fiber makes your body break down food more slowly. This helps release energy gradually instead of all at once. When your energy releases slowly, you feel steady instead of spiking and crashing.
Prevents Sugar Spikes
When a meal has little to no fiber, your blood sugar rises too fast. This leads to a crash later. Fiber smooths out these rises so you don’t hit that midmorning or midafternoon slump.
Feeds Gut Bacteria That Produce Energy-Supporting Compounds
Healthy gut bacteria turn fiber into short-chain fatty acids. These compounds help your body reduce inflammation, regulate appetite, and maintain balanced energy throughout the day.
Supports Hormones That Regulate Energy
Fiber helps keep insulin and cortisol levels steady. Those hormones play big roles in keeping your mood and energy stable.
What Happens When Fiber Is Too Low
Low-fiber meals digest quickly. That may feel good at first, but the fast digestion leads to problems.
Digestion Moves Too Fast
Your body burns through fuel quickly, which means hunger returns sooner. Fast hunger leads to constant snacking and more crashes.
Bigger Blood Sugar Swings
Low-fiber foods cause big energy spikes, followed by sharp drops. These drops make you feel:
- Shaky
- Irritable
- Tired
- Unfocused
Higher Inflammation
Low fiber often means fewer antioxidants and fewer good gut bacteria. This increases inflammation, which drains energy.
Worse Gut–Brain Communication
Your gut plays a huge role in your mood and energy. Without fiber, the gut struggles to send steady, healthy signals to your brain.
Signs Your Energy Issues Are Linked to Low Fiber
Low fiber affects people in different ways, but some signs show up often.
You may be low in fiber if you notice:
- Feeling tired after meals
- Midday energy crashes
- Constant cravings
- Big hunger swings
- Trouble focusing
- Brain fog
- Needing caffeine to stay alert
- Irritability when hungry
These symptoms often improve simply by adding more fiber to your meals.
How Fiber Helps With Blood Sugar Control
Blood sugar stability is one of the biggest keys to stable energy.
Slows Down Carbohydrate Breakdown
Carbs without fiber digest quickly and spike blood sugar. Fiber slows this process so your blood sugar stays balanced.
Prevents Crashes
When blood sugar drops too fast, your energy plummets. Fiber helps prevent this by reducing how fast sugars enter your bloodstream.
Supports Insulin Sensitivity
Fiber helps your body use insulin more efficiently. Better insulin control means smoother, more predictable energy.
Gut Health, Fiber, and Energy
Your gut is home to trillions of bacteria that influence how you feel. When they’re healthy, they help keep your mood and energy stable.
Fiber Feeds Healthy Gut Bacteria
When gut bacteria have enough fiber, they help your digestion work smoothly and keep inflammation low.
Short-Chain Fatty Acids Boost Energy
When bacteria break down fiber, they produce short-chain fatty acids. These help:
- Reduce inflammation
- Improve blood sugar control
- Support steady hunger levels
Low Fiber Creates Imbalance
Without fiber, harmful bacteria can grow too quickly. This often leads to fatigue, bloating, and irregular digestion—all of which affect energy.
Best High-Fiber Foods for All-Day Energy
Adding fiber doesn’t have to be complicated. The best foods are whole, simple, and easy to include.
Whole Grains
- Oats
- Quinoa
- Brown rice
- Barley
- Whole-grain bread
Fruits
- Apples
- Pears
- Berries
- Oranges
- Bananas
Vegetables
- Sweet potatoes
- Carrots
- Broccoli
- Leafy greens
- Peas
Legumes
- Lentils
- Chickpeas
- Black beans
- Kidney beans
Nuts & Seeds
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds
- Almonds
- Pumpkin seeds
These foods pair well with proteins and healthy fats to create balanced, energizing meals.
What to Eat Instead of Low-Fiber Foods
Simple swaps can make a huge difference in how you feel each day.
Breakfast Swaps
- Instead of sugary cereal → oatmeal with berries
- Instead of white toast → whole-grain toast with avocado
- Instead of a muffin → yogurt bowl with chia seeds and fruit
Lunch Swaps
- Instead of white rice → quinoa or brown rice
- Instead of deli sandwiches → whole-grain wrap with veggies and beans
- Instead of fast food → lentil soup or a grain bowl
Snack Swaps
- Instead of chips → nuts or fruit
- Instead of candy → apple slices with nut butter
- Instead of crackers → veggies with hummus
Dinner Swaps
- Instead of white pasta → whole-grain pasta
- Instead of heavy takeout → veggie stir-fry with brown rice
- Instead of fries → roasted sweet potatoes
Small upgrades lead to big energy improvements.
Simple High-Fiber Meal Templates
A balanced meal helps keep your energy smooth and predictable.
The 3-Part Plate
- Fiber-filled carbs (fruits, veggies, whole grains)
- Lean protein (chicken, fish, tofu, beans)
- Healthy fats (avocado, nuts, olive oil)
This combination slows digestion, balances blood sugar, and keeps you full for hours.
How Much Fiber You Need for Better Energy
Most adults should aim for:
- About 25 grams per day for women
- About 38 grams per day for men
Most people get less than half.
How to Increase It Safely
- Add fiber slowly
- Drink plenty of water
- Spread fiber throughout the day
- Mix different fiber types
These steps help your gut adjust comfortably.
Common Mistakes People Make
Adding Too Much Fiber Too Quickly
This can lead to:
- Gas
- Bloating
- Cramping
Increase fiber gradually to prevent discomfort.
Not Drinking Enough Water
Fiber needs water to move through the digestive system.
Relying Only on Supplements
Supplements help, but whole foods provide better energy and more nutrients.
Eating Fiber Without Protein
Fiber works best when paired with protein and healthy fat.
FAQs
Can too much fiber make you tired?
Only if you increase it too fast. Slow increases are best.
Why do carbs make me sleepy?
Low-fiber carbs spike your blood sugar. The crash makes you feel tired.
How fast does fiber improve energy?
Many people feel better within 1–2 weeks.
Final Takeaway
Low fiber is one of the most overlooked causes of energy crashes. Fiber helps steady your digestion, balance blood sugar, support gut health, and regulate hormones—all of which help you feel energized throughout the day.
Adding fiber-rich foods to every meal is one of the simplest ways to boost energy, reduce cravings, and stay focused from morning to night.